This complete guide to the CPF Ordinary Account (OA) will take you through what the OA entails, its interest rates, what it can be used for, repayment and investment options, as well as some frequently asked questions.
What is the CPF Ordinary Account?
The CPF OA is 1 out of the 3 accounts in Singapore’s national saving scheme. Besides using the CPF OA to grow your retirement savings, you may tap into its funds to pay for housing, education and insurance.
The CPF OA is where most of your CPF contributions are channelled to when you earn your monthly salary.
The proportion of monthly CPF contribution your OA receives is dependent on your age.
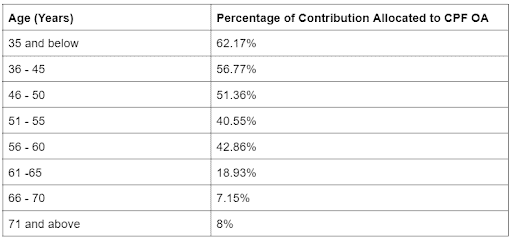
Once you turn 55 years old, the funds in your OA will be combined with funds in your CPF Special Account (CPF SA) to form your CPF Retirement Account (CPF RA).
CPF Ordinary Account Interest Rates
The first $20,000 in your OA will yield an interest rate of 3.5%. Subsequently, your CPF OA will accrue 2.5% interest per annum.
The interest earned will be deposited into your CPF account at the end of every year.
What can I use my Ordinary Account For?
Your CPF OA can be utilised to fulfil housing, education, and insurance payments.
Before you tap into the funds of your CPF OA, you will need to consider the minimum balances required:
- Housing and Insurance: None; however, a balance of $20,000 is recommended as an emergency fund.
- Education (CPF Education Loan Scheme): The annual withdrawal limit. However, if you are 55 or older, you need the Full Retirement Sum (FRS) in your CPF RA.
Housing
Under the CPF Housing Scheme, you may mobilise your CPF OA funds for the following purposes:
- Purchase of HDB flat
- Purchase or building of private residential property
- Downpayment of your purchased property
- Housing loans, or loans undertaken for home construction or vacant land purchase
- Stamp and legal fees
Education
Under the CPF Education Loan Scheme, you may utilise your CPF OA up to the Available Withdrawal Limit (AWL).
The AWL is computed as the lower of the following:
- 40% of total CPF OA savings, that is, the sum of your current OA balance and all previously funds withdrawn for education and investment purposes
- Remaining CPF OA balance, excluding any funds set aside for housing or other schemes
The percentage of your CPF OA that you are entitled to mobilise for the financing of education is dependent on whose education you are paying for.
If you are using your CPF OA to fund your own, your sibling’s, spouse’s or children’s education, you are entitled to utilise 100% of the AWL.
If you are using your CPF OA to fund your relative’s education, you are only allowed to mobilise:
- 10% of your CPF OA for their studies at the university level
- 25% of your CPF OA for their education at polytechnic level or diploma studies (Technical Engineer Diploma or Technical Diploma in Culinary Arts at ITE)
- 50% of your CPF OA for their education at an art college
Insurance
Dependants’ Protection Scheme (DPS)
Your CPF OA may be used to pay insurance premiums under the Dependants’ Protection Scheme (DPS).
Solely offered by Great Eastern Life, the DPS is a term life insurance that provides you and your family financial protection in unexpected events of total permanent disability, terminal illness, or death.
You will automatically be enrolled unless you choose to opt-out from it.
Home Protection Scheme (HPS)
The HPS is an affordable housing insurance which offers one of the lowest premiums in the market. It safeguards you from outstanding housing or mortgage loans in the occurrence of total permanent disability, terminal illness, or death.
You are eligible for the HPS:
- If you are between 21 to 65 years old.
- If you are an owner of an HDB flat. Private residential property owners may only be covered by private housing insurance.
- If you make housing payments in monthly instalments via CPF savings or cash. For homeowners using CPF savings for housing payments, HPS is compulsory.
- If you are in good health. You may be requested to undergo a medical examination and submit the medical results. Should you not meet the health requirements, you will still be able to mobilise your CPF savings for monthly housing instalments.
You will be insured by the HPS till you turn 65 years old or till your housing loans are fulfilled, whichever is earlier. To continue insuring your flat beyond age 65, you may purchase private housing insurance.
The premium payable for HPS is computed based on the following:
- Loan amount
- Type of loan interest (market or concessionary rate)
- Loan term (in years)
- Percentage of coverage
Annual HPS premiums will be automatically fulfilled using your CPF OA. You may authorise for HPS premiums to be paid by your co-owner’s CPF OA should the funds in your account be insufficient. This is provided that your co-owner is your family member, that is, your spouse, parent, child, or sibling.
According to the HPS premium calculator, a male aged 35 years old taking a concessionary loan of $400,000 with a loan tenure of 25 years would expect to pay $384 a year in HPS premiums.
The premiums for Home Protection Scheme can be fully paid using our CPF Ordinary Account. The deductions for HPS take priority over our housing loan instalment. If we have insufficient funds, the co-owners of our flat can also be authorised to use their OA savings to pay for the premiums.
Repaying Your CPF OA
CPF Refund Upon Property Sale or Transfer
Suppose you decide to sell or transfer your property to another party. In that case, you must refund the sum of the principal amount withdrawn from your CPF OA for the property purchased and the accrued interest.
Suppose any option monies such as option fees and option exercise fees were mobilised. In that case, you will need to refund them to your own and your co-owner’s CPF account since they comprise the property’s selling price.
If you sold your property at market value, you would not need to top up the shortfall. This is provided that the selling price (inclusive of option monies) is not enough to refund the amount utilised with accrued interest after fulfilling your outstanding loan.
Funds will be distributed to you and your co-owner in proportion to the amount of CPF savings used.
When selling your share of the property, it must be transacted at market value. Should the selling price be insufficient to refund your CPF OA after repaying your percentage of the loan, the amount to be refunded will be the greater of the following:
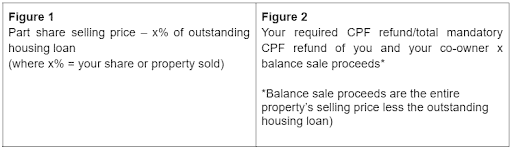
The refund amount is capped at the sum of the principal amount withdrawn from your CPF OA for the property purchased and the accrued interest.
Should you be 55 years old and above and have pledged your property to form part of your retirement sum, you will also need to repay the pledged amount.
This amount will contribute towards your FRS in your CPF RA. Should there be any residual funds, they will be reimbursed to you via cash within one week after the refunds have been credited into your CPF.
Voluntary Housing Refund
Suppose you have mobilised your CPF OA for housing payments. In that case, you may make a voluntary housing refund to your CPF OA even if you are not selling your property.
By doing so, you are leveraging the interest of your CPF OA, yielding you more returns for more significant retirement savings.
Additionally, you can mobilise the refunded amount for other CPF-approved housing, education, insurance and investment schemes.
Since you have made repayments to your CPF OA now, you will have lesser refunds to make in the future when you sell your property.
This enables you to obtain profits when you sell your property.
The maximum amount you may repay to your CPF is the sum of the principal amount withdrawn from your CPF OA for the property purchased and the accrued interest.
Investing your OA funds
Investing the funds in your CPF OA is a good way to beat the 2.5% risk-free rate. Funds in your OA are investible once you set aside a minimum balance of $20,000.
Under the CPF Investment Scheme (CPFIS), you may grow your retirement savings by investing the funds in your CPF OA and SA into the following investment products:
- Unit Trusts (UTs)
- Investment-linked insurance products (ILPs)
- Annuities
- Endowment policies
- Singapore Government Bonds (SGBs)
- Treasury Bills (T-bills)
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Fund Management Accounts
- Fixed deposits
- Stocks*
- Property Funds*
- Corporate Bonds*
- Gold ETFs**
- Other Gold products (e.g. Gold certificates and savings accounts, Physical Gold)**
*May only utilise up to 35% of investible savings
**May only utilise up to 10% of investible savings
(Investible savings is calculated by adding your CPF OA balance to the amount withdrawn from your CPF for investment and education)
You may embark on your CPFIS-OA investment journey by opening a CPF Investment Account with a CPFIS agent bank. CPFIS agent banks include:
- DBS Bank Ltd (DBS)
- Overseas-Chinese Banking Corporation Ltd (OCBC)
- United Overseas Bank Ltd (UOB)
Find out more about CPFIS in our comprehensive guide!
Conclusion
In summary, the CPF OA enables account holders to grow their retirement savings from the interest it yields and the investment products under the CPFIS. It can also be used to alleviate housing, education, and insurance obligations.
Speak to our accredited financial advisors to understand how you can best mobilise your CPF OA funds for your personal needs!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I withdraw funds from my CPF OA?
You will not be able to withdraw funds directly from your CPF OA. That being said, you will be able to make withdrawals from your CPF RA upon reaching 55 years old. Your CPF RA is made up of the monies in your CPF OA and SA.
Can I top up my CPF OA?
While topping up your CPF OA solely is not permitted, you may deposit funds into your CPF as a whole, and it will be allocated to your 3 respective CPF accounts – CPF OA, SA, and Medisave.
Allocations are made following the allocation rates for mandatory CPF contributions.
The top-up limit is computed by taking the CPF Annual Limit ($37,740) less the mandatory CPF contributions made for the calendar year.
What is the difference between the CPF OA and CPF SA?
The CPF OA aims to set aside funds to fulfil financial obligations – housing, education, insurance, and investment. On the other hand, the CPF SA focuses on accumulating savings for retirement. Funds in the CPF SA can be mobilised for retirement-related financial and investment products.
Keen to understand more about the CPF SA? Check out our ultimate guide!
References
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/cpf-overview
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/faq/growing-your-savings/cpf-interest-rates/what-are-the-cpf-interest-rates
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/home-ownership/using-your-cpf-to-buy-a-home/retain-20000-in-your-oa-if-you-are-taking-a-housing-loan
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/home-ownership/using-your-cpf-to-buy-a-home
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/home-ownership/protecting-against-losing-your-home
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/faq/other-schemes/cpf-education-loan-scheme/how-much-ordinary-account–oa–savings-can-i-use-under-the-cpf-e
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/faq/other-schemes/cpf-education-loan-scheme/how-much-of-tuition-fees-can-be-paid-using-ordinary-account–oa-
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/account-services/providing-for-your-loved-ones/insuring-to-protect-your-dependants
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/home-ownership/using-your-cpf-to-buy-a-home/cpf-refund-when-selling-or-transferring-property
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/growing-your-savings/saving-more-with-cpf/make-a-voluntary-housing-refund
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/growing-your-savings/earning-higher-returns/investing-your-cpf-savings
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/faq/growing-your-savings/top-up-your-cpf-accounts-to-build-your-savings/can-i-voluntarily-top-up-to-my-ordinary-account-only
- https://www.cpf.gov.sg/member/growing-your-savings/saving-more-with-cpf/top-up-ordinary-special-and-medisave-savings